Library
Starbase Corinth IV
In 2266, the U.S.S. Enterprise NCC-1701 was scheduled to visit Starbase Corinth IV, where Commodore Jose Dominguez eagerly awaited an “urgent” delivery of Mexican red chili peppers from his friend, Captain James T. Kirk.[1]
References
Starbase 9

Starbase 9 (TOS DC v2 73)
Originally a supply station constructed in the 2180s, Starbase 9 slowly became a major scientific and astronomical monitoring station — the Argus Array, for example, was designed as an “uprated” model of Starbase 9’s orbital phased EM collectors.[2]
The U.S.S. Stargazer NCC-2893 was towed to this starbase after the U.S.S. Enterprise NCC-1701-D received the old vessel from the Ferengi in 2364.[1]
References
- 1. “The Battle.” Star Trek: The Next Generation, Episode 110. Television. 16 November 1987.
- 2. “Starfleet Operations Manual.” Star Trek Roleplaying Game, Book 3. Game. 2003. Decipher, Inc.
Stameris
Planet known for its slave market in the mid-22nd century. Ulis and his Ferengi crew planned to sell the female crewmembers of the Enterprise NX-01 at a slave market on this planet.[1]
References
Sol System

Sol (ST-04)

Sol (TOS-21)
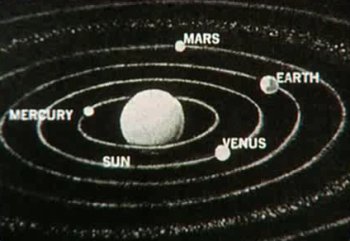
Sol System (TOS-00)
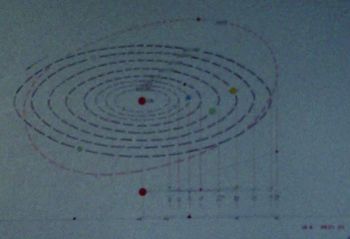
Sol System (TOS-37)
Star system located in Sector 001, in the Alpha Quadrant. The parent star, Sol, was Type-G and was orbited by eight planets (though Pluto frequently switched between being considered a planet and a planetoid),[2] including Earth, and was commonly known as the Sun. The Talosians viewed an image of the Sol System and many images of Earth’s history while accessing the U.S.S. Enterprise NCC-1701‘s computer in 2254.[1]
Planets
References
- 1. “The Cage.” Star Trek, Episode 0. Television. 1965 (Unaired).
- 2. “Before Dishonor.” Star Trek: The Next Generation. Novel (Unnumbered). November 2007.
Sector Zones
Quadrants were divided into numbered Subquadrants and Sector Zones. The intersection of a subquadrant and a sector zone resulted in a roughly cube-shaped Sector Grid, which was 5000 light years long and 3600 light years high along the galactic plane; the width varied by distance from the galactic core—at the rim, it could be as wide as 8727 light years. Each sector grid was then divided into a cubic grid of 100 Sector Quads, which were then further broken down into 900 ore more roughly cubical Sector Blocks, each measuring nearly 100 cubic light years (varying by distance from the galactic core). Finally, sector blocks were divided into 100 sectors, each measuring 20 cubic light years.Sector numbers were a nine-digit sequence with the first two digits representing the sector grid, the first digit of which represented the subquadrant and the second the sector zone (e.g. Sector Grid 15 was the intersection of subquadrant 1 and sector zone 5); the next two digits represented the sector quad; the next three digits represented the sector block; and the final two digits represented the sector proper.[1]
References
Sector Quads
Quadrants were divided into numbered Subquadrants and Sector Zones. The intersection of a subquadrant and a sector zone resulted in a roughly cube-shaped Sector Grid, which was 5000 light years long and 3600 light years high along the galactic plane; the width varied by distance from the galactic core—at the rim, it could be as wide as 8727 light years. Each sector grid was then divided into a cubic grid of 100 Sector Quads, which were then further broken down into 900 ore more roughly cubical Sector Blocks, each measuring nearly 100 cubic light years (varying by distance from the galactic core). Finally, sector blocks were divided into 100 sectors, each measuring 20 cubic light years.Sector numbers were a nine-digit sequence with the first two digits representing the sector grid, the first digit of which represented the subquadrant and the second the sector zone (e.g. Sector Grid 15 was the intersection of subquadrant 1 and sector zone 5); the next two digits represented the sector quad; the next three digits represented the sector block; and the final two digits represented the sector proper. Prior to the mid-24th century, sector quads were commonly, though erroneously, referred to as “quadrants.” This practice fell into disuse, however, due to the widespread confusion it often generated.[1]
References
Sector Grids
Quadrants were divided into numbered Subquadrants and Sector Zones. The intersection of a subquadrant and a sector zone resulted in a roughly cube-shaped Sector Grid, which was 5000 light years long and 3600 light years high along the galactic plane; the width varied by distance from the galactic core—at the rim, it could be as wide as 8727 light years. Each sector grid was then divided into a cubic grid of 100 Sector Quads, which were then further broken down into 900 ore more roughly cubical Sector Blocks, each measuring nearly 100 cubic light years (varying by distance from the galactic core). Finally, sector blocks were divided into 100 sectors, each measuring 20 cubic light years. Sector numbers were a nine-digit sequence with the first two digits representing the sector grid, the first digit of which represented the subquadrant and the second the sector zone (e.g. Sector Grid 15 was the intersection of subquadrant 1 and sector zone 5); the next two digits represented the sector quad; the next three digits represented the sector block; and the final two digits represented the sector proper.[1]
References
Sector Blocks
Quadrants were divided into numbered Subquadrants and Sector Zones. The intersection of a subquadrant and a sector zone resulted in a roughly cube-shaped Sector Grid, which was 5000 light years long and 3600 light years high along the galactic plane; the width varied by distance from the galactic core—at the rim, it could be as wide as 8727 light years. Each sector grid was then divided into a cubic grid of 100 Sector Quads, which were then further broken down into 900 ore more roughly cubical Sector Blocks, each measuring nearly 100 cubic light years (varying by distance from the galactic core). Finally, sector blocks were divided into 100 sectors, each measuring 20 cubic light years. Sector numbers were a nine-digit sequence with the first two digits representing the sector grid, the first digit of which represented the subquadrant and the second the sector zone (e.g. Sector Grid 15 was the intersection of subquadrant 1 and sector zone 5); the next two digits represented the sector quad; the next three digits represented the sector block; and the final two digits represented the sector proper.[1]
References
Sectors
Quadrants were divided into numbered Subquadrants and Sector Zones. The intersection of a subquadrant and a sector zone resulted in a roughly cube-shaped Sector Grid, which was 5000 light years long and 3600 light years high along the galactic plane; the width varied by distance from the galactic core—at the rim, it could be as wide as 8727 light years. Each sector grid was then divided into a cubic grid of 100 Sector Quads, which were then further broken down into 900 ore more roughly cubical Sector Blocks, each measuring nearly 100 cubic light years (varying by distance from the galactic core). Finally, sector blocks were divided into 100 sectors, each measuring 20 cubic light years. Typically, a sector contained approximately 40 stars, about two-thirds of which were part of binary, trinary, or even quadrinary systems. However, in dense globular star clusters, a sector may have contained several thousand stars, and in the void between spiral arms, sectors may have contained no stars at all.[2]
› Continue reading
Saturn

Saturn (TNG-101-102)
Saturn was the sixth planet in the Sol System. The Talosians viewed an image of the Sol System while accessing the U.S.S. Enterprise NCC-1701‘s computer in 2254.[1]
References
Categories
- Animated Series (60)
- Articles (28)
- Books (447)
- Cast & Crew (79)
- Comics (22)
- DS9 (328)
- Early Voyages (125)
- Education (5)
- Enterprise (373)
- Excelsior (36)
- Food (19)
- Games (223)
- Klingon (70)
- Library (1,543)
- Logs (593)
- Lost Era (55)
- Medicine (18)
- Merrimac (1)
- Mirror (35)
- Miscellaneous (13)
- New Frontier (54)
- Next Generation (635)
- Original Series (681)
- Personnel (436)
- Places (369)
- Politics (12)
- Recreation (10)
- SCE (41)
- Science (1)
- Shatnerverse (9)
- Ships (455)
- Site Updates (98)
- Starfleet Academy (86)
- Stargazer (42)
- STO (61)
- Technology (45)
- Titan (59)
- To Boldly Go (1)
- TV/Film (214)
- Uncategorized (4)
- Vanguard (76)
- Voyager (236)
- Weapons (27)
- Xenology (54)